
What is Embedded Insurance: A Straightforward Guide
Embedded insurance is one of the hottest trends in the industry in 2024.
It allows companies to integrate insurance products into their sales processes, delivering value to customers right at the point of purchase.
Let’s explore how embedded insurance works, its benefits, and why it’s changing the way businesses and consumers think about insurance.

What is Embedded Insurance?
People recognize the need for insurance, but it’s generally viewed as a burdensome afterthought or legal requirement that often feels confusing and overwhelming to the average customer.
That’s where embedded insurance comes in.
This new way of packaging and selling insurance products aims to seamlessly integrate insurance purchases into everyday transactions.
It offers immediate protection at the point of sale, making the process quicker and more convenient.
Closing the Protection Gap
Why is embedded insurance an important trend?
At a strategic level, embedded insurance helps to address the growing global “protection gap” – the difference between the coverage people need and what they actually purchase.
According to the latest report by Sigma, just 38% of the global economic losses, amounting to USD 108 billion out of a total of USD 280 billion, were covered by insurance.
These gaps highlight a huge opportunity for non-insurance brands to partner with the insurance industry, using embedded insurance to engage customers in new ways and close these gaps.
In addition, younger generations accustomed to the ease and convenience of digital platforms are demanding the same level of customer experience when purchasing insurance products.

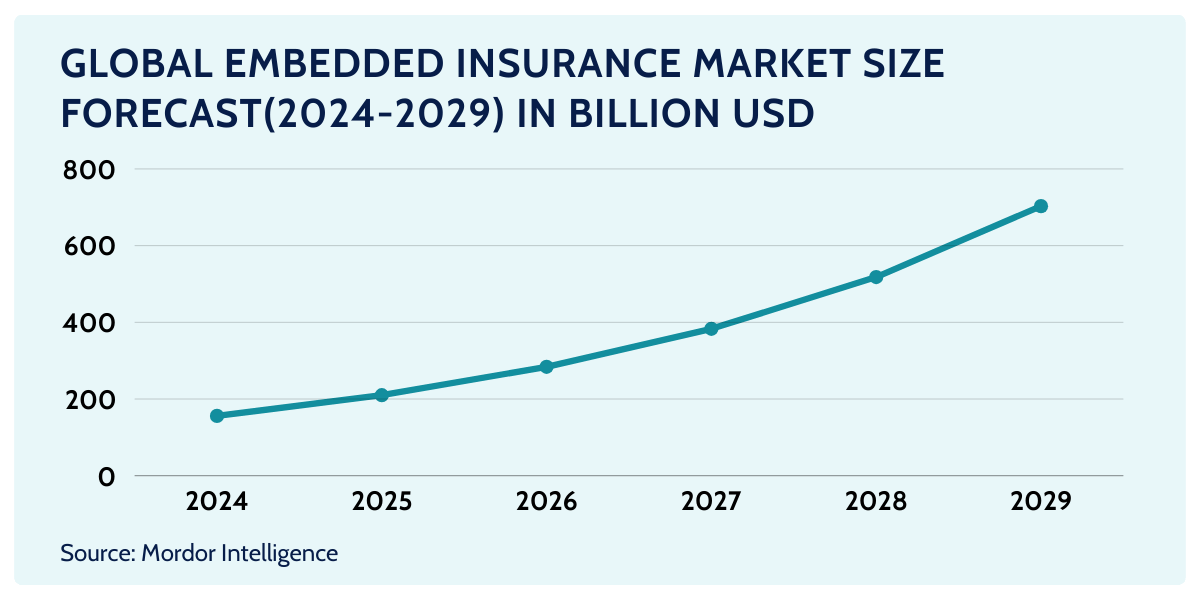
Embedded Insurance Market: $3 Trillion Opportunity for Brands and Insurers
The embedded insurance market has significant growth potential in the coming years.
According to the latest embedded insurance trends and statistics, in the property and casualty sector alone, embedded insurance is expected to grow at a CAGR of 25% to 2030, potentially reaching over $500 billion in global premiums, or 20% of the total market.
Including life and health insurance, embedded insurance could generate more than $3 trillion in market value – that is to the benefit of companies that embrace it.
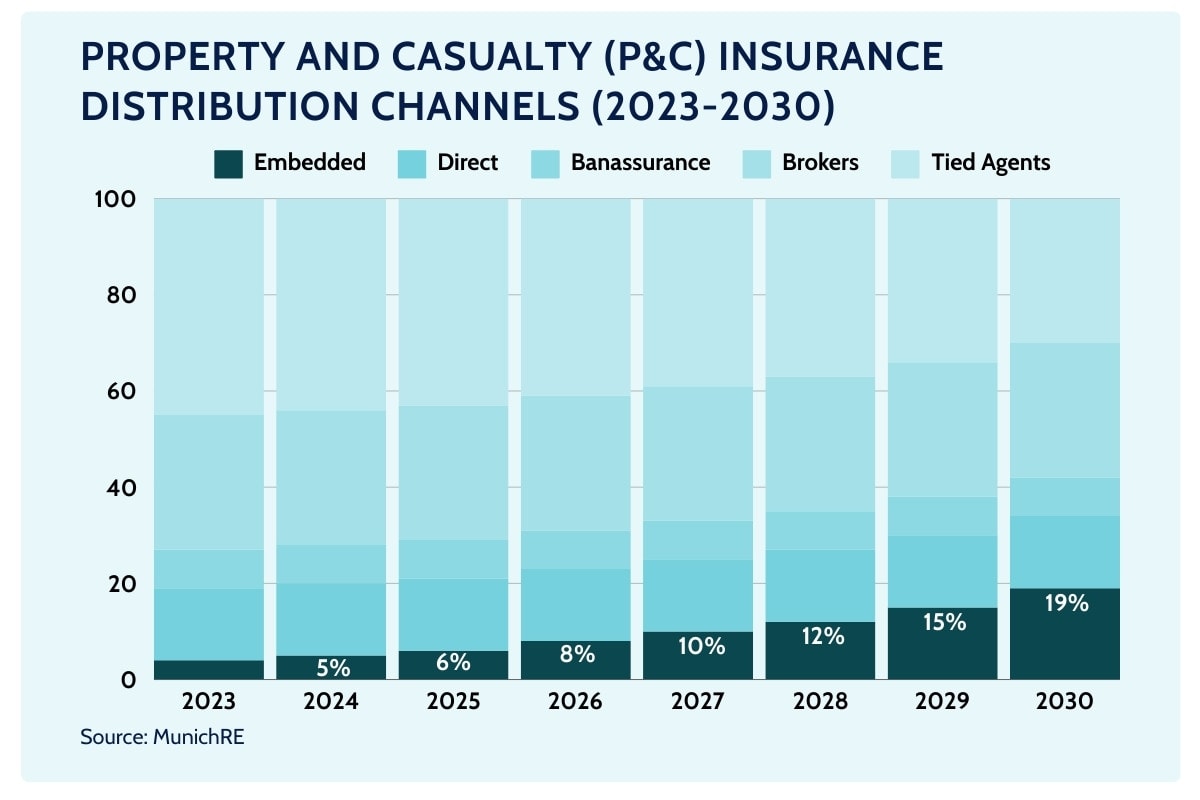
According to Aperture, up to $5 trillion of insurance could be distributed by non-insurance brands over the next decade. This would grow from less than 1% of the total market today to 4-5% by 2027 and potentially 16% by 2032.
This shift presents a great opportunity to open new distribution channels, like embedded, while improving the customer experience.
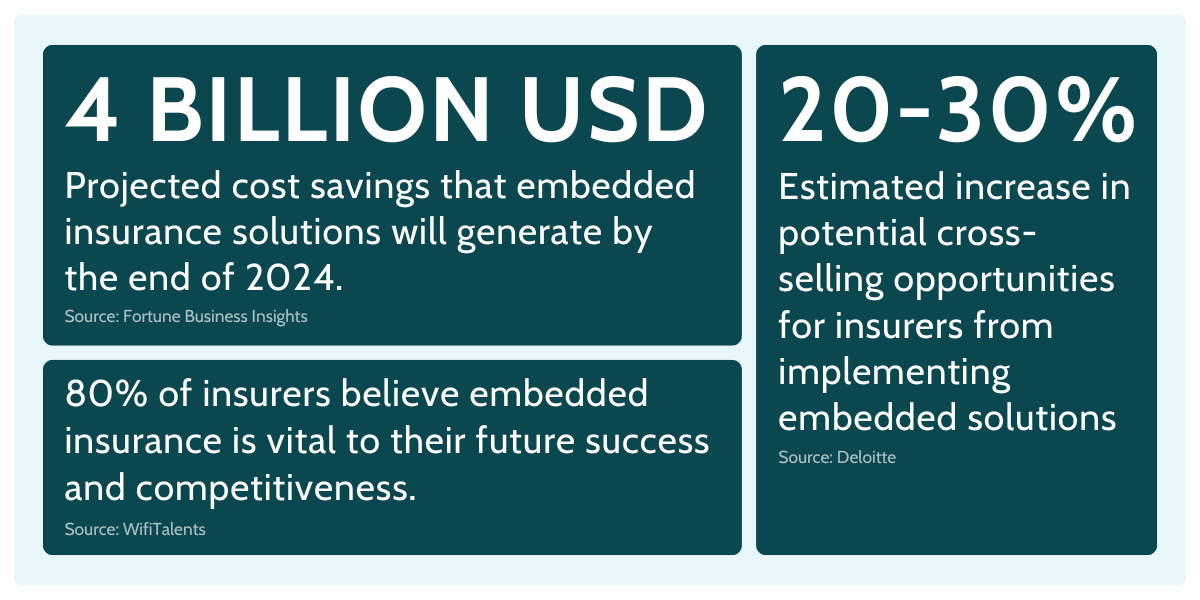
Many insurance industry professionals have already noticed immense potential that embedded solutions hold for the future of this industry.
According to Adacta 94% of insurance professionals recognized embedded insurance as a vital component of their future planning.
One DACH respondent from their study stated, “Providing tailor-made insurance products and services that cater to individual needs and behaviors will become paramount in the coming years.”
This highlights the industry’s shift from being reactive to proactive, with a focus on precisely meeting the varied needs of today’s consumers.
How Different Industries Use Embedded Insurance
In various industries, embedded insurance has been present for many years, generating a steady stream of additional revenue to companies that decided to introduce this practice.
Let’s take a look at the most popular examples:
- Travel Industry – In the travel sector, travel insurance is often offered as part of the booking process hotels, vacation packages or plane ticket purchase. On Booking, AirBnB and Ryanair you can easily add trip protection, cancellations, or baggage coverage with just a click, ensuring peace of mind without needing to navigate separate insurance policies.
- Ecommerce Industry – Many online retailers offer purchase coverage by integrating insurance for items like electronics or furniture, enabling customers to protect their purchases from damage, theft, or loss at the point of sale with just a few clicks.
- Telecom Industry: Companies like Verizon and AT&T embed cellphone insurance when customers purchase new devices, offering protection plans that cover accidental damage, theft, or loss, often included during the device checkout or through monthly billing.
- Automotive Industry – Car manufacturers and dealerships integrate car insurance into the purchase or leasing process, providing immediate coverage options for new vehicles.
Tesla Case: How Embedded Insurance Creates Value At Unprecedented Scale
Tesla is a prime example of an automotive company that integrate insurance coverage into their product offering.
By utilizing data collected from its vehicles’ embedded systems, Tesla has ventured into the insurance industry, offering its own embedded insurance products.
In 2024 in certain U.S. states, 17% of Tesla customers already use Tesla’s own insurance offering.
What’s more surprising, it’s the sheer value of revenue generated from its insurance offerings.
Tesla itself predicts that embedded insurance could account for 30–40% of the company’s total future value. For an automotive company of that size, it’s a huge percentage.
Industry experts, such as those at GlobalData, foresee car insurance as one of the sectors most likely to experience significant disruption due to embedded coverage. Research also indicates that within the next 10 to 20 years, 40% of insurance will likely be embedded within other products and services.
The Value of Embedded Insurance for Business
Before integrating embedded solutions, you should take into considerations not only all the benefits and opportunities, but also the difficulties connected with that unique way of reaching new customers.
Benefits
Offering embedded insurance benefits both clients and companies.
For clients, it provides seamless, convenient coverage right at the point of sale, without the need to seek out traditional insurance separately.
This creates a smoother customer experience, where protection is bundled into their purchase.
For companies, it opens up new revenue streams, increases customer loyalty, and differentiates their offerings.
By integrating insurance directly into their services, businesses can enhance customer trust while reducing friction in the buying process.

Opportunities
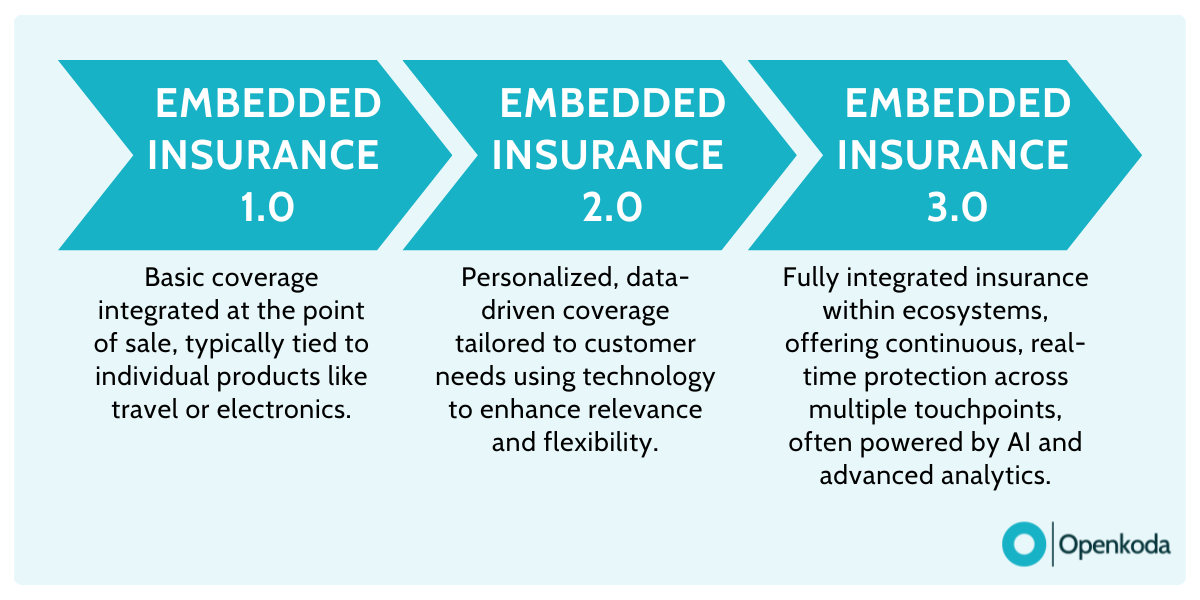
As technology continues to improve, companies are coming up with more innovative ways of embedding insurance products in various business.
The initial “Version 1.0” of embedded insurance has been around for quite a long time. A great example is purchasing life insurance before a flight – a business model that turned into an incredibly profitable business.
As consumers began to purchase more and increasingly expensive items, we arrived at “Version 2.0” of embedded, where customers could seamlessly add on insurance while they’re making a physical purchase.
Now Version 3.0 is entering the market.
Accenture defines this generation as insurance becomes an integral part of commercial transactions. The client does not modify it – everything is done automatically in the background.
Embedded Insurance AI dynamically calculates premiums while clients don’t even modify the details of the offer.
Volvo’s EX40 electric vehicle insurance in partnership with Allianz or Spot’s injury insurance being included in ski passes are great examples of this concept in practice.
Challenges
While embedded insurance offers convenience and value, it also presents challenges for non-insurance brands.
Companies typically lack in-house expertise in the complexities of insurance, making it difficult to navigate regulatory and legal requirements.
Policy claims management, compliance, and customer service can also become overwhelming, requiring specialized knowledge that many businesses are not equipped with internally.

How Embedded Insurance Works
Embedded insurance works by including a seamless way to offer coverage directly within the purchase process.
Customizable insurance forms are integrated into the checkout pages of ecommerce sites, OTAs, and similar platforms using APIs or plugins, allowing for easy adjustment based on the specific purchase.
These forms dynamically calculate fees and prices for the insurance product in real-time by pulling data from both the customer’s purchase details and pre-set insurance pricing models.
This streamlined approach eliminates the need for separate transactions and simplifies the decision-making process, making it easy to opt for insurance without leaving the platform.
[Read also: How Embedded Insurance Enables Personalized Protection]
How to Implement Embedded Insurance?
The process of implementing embedded insurance depends on whether you represent an insurance company or another business looking to cross-sell insurance products.
Regardless of which side your organization falls on, using software development platforms with pre-built insurance components like Openkoda can reduce custom insurance software development time by up to 60%, allowing you to bring your solution to market faster.
Openkoda provides a system that enables the creation of various types of embedded forms tailored to different industries (e.g., e-commerce, travel, mobility, finance). These forms are easily customizable and can be seamlessly integrated with insurers’ APIs to dynamically calculate insurance premiums.
Check this tutorial to learn how to build an embeddable quote form with Openkoda.
Unlike many other embedded insurance providers, Openkoda’s technology is open-source, there’s no vendor lock-in. You own the code, and because there’s no proprietary language, you have the flexibility to choose your own hosting, apply your branding, or leverage managed cloud services.
If your business prioritizes cost efficiency, scalability, personalization, and flexibility, Openkoda offers a highly convenient approach to introducing embedded insurance.
