
7 Key Insurtech Trends For 2025
The pace of development in the insurance industry has been accelerating for quite some time, driven by key trends like custom software solutions or artificial intelligence.
These and other trends pose a clear challenge to insurers: ace digital transformation or risk falling behind tech-savvy insurtech disruptors.
let’s take a look at the key insurance technology trends driving that change in 2025 and beyond.

Contents
- The State of Insurtech in 2025
- Trend #1: Embedded Insurance Growth
- Trend #2: AI-Powered Insurance Functionalities and Chatbots
- Trend #3: Smart Custom Insurance Application Development
- Trend #4: Self-Service for Policyholders
- Trend #5: Modernizing Legacy Insurance Systems
- Trend #6: Usage-Based Insurance and Claims
- Trend #7: Emerging Risks
The State of Insurtech in 2025
Once a niche offshoot of the broader insurance sector, insurtech has become a major force reshaping how insurance is developed, distributed, and experienced as more and more insurers are turning to technology to stay ahead.
Recent industry data highlights this trend: In a survey of 120 insurance leaders, 78% said they plan to increase their technology budgets, with 36% prioritizing artificial intelligence (AI) initiatives.
Customers are also accelerating this shift. With the rise of digital-native policyholders, seamless digital experiences have become a baseline expectation rather than a competitive advantage. Nearly 80% of customers now cite a smooth, intuitive claims process as a key factor in choosing or staying with an insurer.
In this environment, both traditional carriers and insurtech startups face mounting pressure to innovate.
Trend #1: Embedded Insurance Growth
More often than not, end users aren’t actively looking to buy insurance.
What they want is to purchase a product or service—and they may consider insurance if it’s conveniently embedded within that same user journey.
Embedded Insurance: Key Insurance Sales Channel in the Coming Years
Embedded insurance is more than just a distribution method—it’s quickly emerging as a primary sales channel within the insurance industry.
By integrating insurance products directly into digital transactions—whether through e-commerce, travel bookings, or financial services—insurers can reach a wider customer base and offer coverage at the exact moment it’s needed.
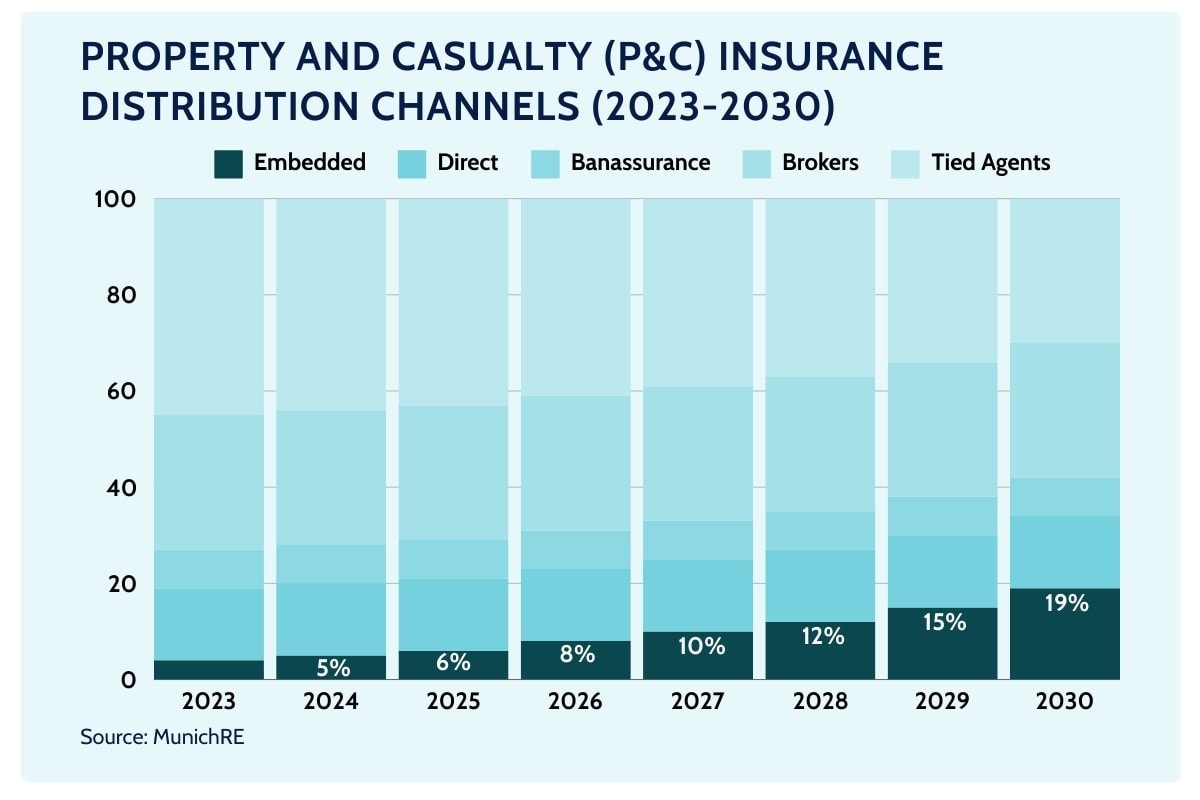
According to the Open Embedded Insurance Report 2024, insurers expect embedded insurance (excluding bancassurance but including B2B2C and affinity models) to grow its share of gross written premiums (GWP) by up to 15% over the next decade—more than any other distribution channel.
In short, for insurers and retailers seeking future growth, embedded insurance stands out as the most promising new sales avenue.
Consumer behavior reflects this shift. Research from Assurant shows that offering an embedded protection plan can boost purchase intent by 25% for retailers and e-commerce platforms.
Two things are worth considering: the correct execution model and personalization.
Execution model
There are currently three main execution models for embedded insurance:
- Bundled: Insurance is included as part of a service plan that the end customer subscribes to.
- Transactional: Insurance is offered contextually—either in real time during the purchase of another product or service, or shortly after the sale.
- Marketplace: Insurance is made available through digital platforms, where distribution partners can integrate it into their own marketplaces, giving customers the option to choose from a range of protection products alongside other services.
Personalization
Embedding insurance into any distribution channel isn’t enough on its own—convenience doesn’t always mean value.
True relevance comes from personalization: offering the right product, at the right time, in the right way—seamlessly and without friction. The key to achieving this lies in leveraging data from earlier steps in the user journey.
Travel insurance is a great example. When booking a flight, customers are offered coverage tailored to their destination, trip length, age, travel purpose, and companions—no extra questions needed.
Creating Customizable Embedded Insurance Forms Quickly and Efficiently
Platforms like Openkoda empower insurance providers to build embeddable, branded forms in days rather than weeks—streamlining onboarding with third-party platforms and significantly accelerating time-to-market.
But what does creating such a form look like in practice?
Imagine you’re a travel agency looking to embed travel insurance options directly into your checkout page.
You’d start by designing a user-friendly form that collects key travel details and presents selectable coverage tiers (e.g., Bronze, Silver, Gold). Next, you’d implement dynamic premium calculation based on inputs like destination and travel dates, enabling real-time quote generation. Add validation rules to ensure data accuracy and securely store the submitted information in your database. Finally, set up automated confirmation emails with a purchase link.
Once complete, the form can be seamlessly embedded on your website—delivering a smooth, interactive experience for your customers.
To learn more details, check out this quick demo:
Trend #2: AI-Powered Insurance Functionalities and Chatbots
Artificial intelligence (AI) is undoubtedly the game-changing technology to watch in the coming years.
In the insurance industry, AI has the potential to transform every part of the value chain—from improving risk assessment and automating claims (already well underway) to redefining the role of insurance agents.
AI-powered Chatbots
Thanks to generative AI, AI-powered chatbots are quickly becoming a standard feature in digital services—especially in health and life insurance.
These bots can handle claims queries, policy updates, customer onboarding, and even guide users through complex forms—all while providing 24/7 support without adding to operational costs.
Here are three noteworthy examples of AI chatbots currently on the market:
- Lemonade’s AI Chatbot, Maya: Helps customers purchase insurance policies and process claims quickly, reducing both policy issuance time and claim payout delays.
- Allstate’s ABIE: Offers personalized guidance to small business owners, explaining various types of business insurance and recommending suitable coverage.
- Zurich Insurance’s Zara: Assists customers in reporting auto and property claims, while also offering advice on insurance policies and home maintenance.
Predictive Analytics and Fraud Detection
Powered by AI and machine learning, predictive models analyze vast amounts of historical and real-time data to identify patterns, trends, and future outcomes with high accuracy.
This is especially valuable in risk assessment and fraud detection.
In underwriting, predictive analytics enables insurers to go beyond basic demographic data, using behavioral signals, transaction history, and lifestyle indicators to assess individual risk and forecast claim likelihood or churn. This supports more personalized premiums and usage-based products.
Fraud detection is another powerful application.
Unlike static, rule-based systems, AI models continuously learn and adapt to evolving fraud tactics.
Take, for example, a health insurance provider using predictive models to detect suspicious billing activity. The AI system notices that a particular clinic consistently bills for complex procedures at a much higher frequency than peer institutions in the same region.
It further identifies that many of these patients visited the clinic only once, yet the bills include ongoing treatments.
Generative AI Report Generation
Capgemini ranks GenAI as the number one insurance industry trend for both P&C and life insurance. According to EY, 42% of insurers are already investing in GenAI, and 57% more are interested or planning to invest.
Among all areas where generative AI can be applied in insurance, report generation and data analytics stand out as the most immediately promising—especially since they’re already feasible with today’s technology and large language models (LLMs).
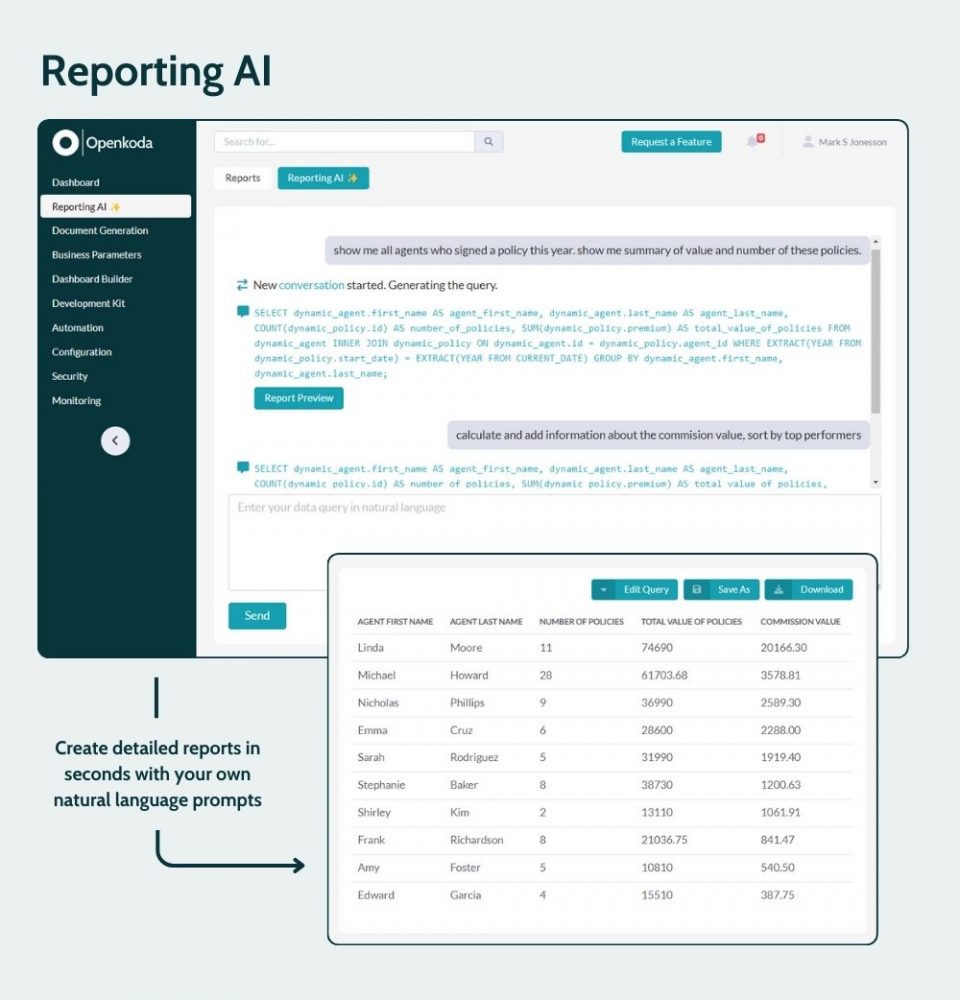
A great example is Openkoda’s Reporting AI – natural language-powered tool that allows users to generate detailed, customizable reports and query application data without writing SQL.
Openkoda takes protecting sensitive customer data very seriously. The system is set up in a way that it sends the LLM API only the database schema without sharing any sensitive customer data.
Thanks to that, the insurer can generate ready SQL queries and execute them locally.
Trend #3: Smart Custom Insurance Application Development
In 2025, custom insurance applications are emerging as a key competitive advantage—enabling everything from real-time policy management to automated claims processing and highly personalized user experiences.
This shift is largely driven by a growing number of customers willing to switch providers due to poor digital experiences. As a result, insurers are under pressure to innovate faster than ever.
But how can insurers balance the high cost of custom insurance software development with the urgent need for innovation?
This is a real challenge.
Building tailor-made solutions from scratch can be expensive and time-consuming, yet off-the-shelf tools often lack the flexibility to meet evolving customer expectations or unique business needs.
While certain core features—like claims intake, quote generation, or policy updates—are essential, reinventing the wheel for every function is neither scalable nor sustainable.
Let’s explore both sides of this challenge and outline a smarter strategy for accelerating custom insurance app development without compromising on quality, flexibility, or cost.
Essential Features of Modern Insurance Application
While each custom insurance application is designed to meet specific business objectives, all successful solutions share a few core elements.
Key features of modern insurance apps include:
- Intuitive, user-friendly interface (UI): Customers and agents alike expect seamless, accessible digital experiences. A clean, intuitive UI boosts engagement and reduces friction across onboarding, quoting, and servicing processes.
- Strong security and data protection: Insurance applications handle highly sensitive personal and financial data. Robust encryption, access controls, and regulatory compliance (such as GDPR or HIPAA, where applicable) are critical.
- Modular architecture: A flexible, modular design allows insurers to adapt quickly to new market demands, integrate third-party APIs, or roll out new product lines without rebuilding the entire system.
- Automation and rules-based workflows: Custom logic that automates underwriting, approvals, or claims decisions helps reduce manual workload and ensures consistency and speed.
- Scalability and performance: Applications must support growth—both in terms of users and data—without compromising speed or reliability.
- Real-time data analytics and reporting: Built-in dashboards and analytics tools help teams make faster, better-informed decisions based on live business data.
Leveraging Insurtech Platforms for Faster Development
Developing a robust insurance application from scratch can be resource-intensive and time-consuming.
To maximize ROI and reduce time-to-market, forward-thinking insurers are increasingly turning to specialized insurtech platforms like Openkoda. These platforms offer pre-built components, integration-ready architectures, and automation features designed specifically for insurance use cases.
Openkoda, for example, accelerates development by up to 60% by combining the flexibility of custom development with the efficiency of ready-to-use building blocks.
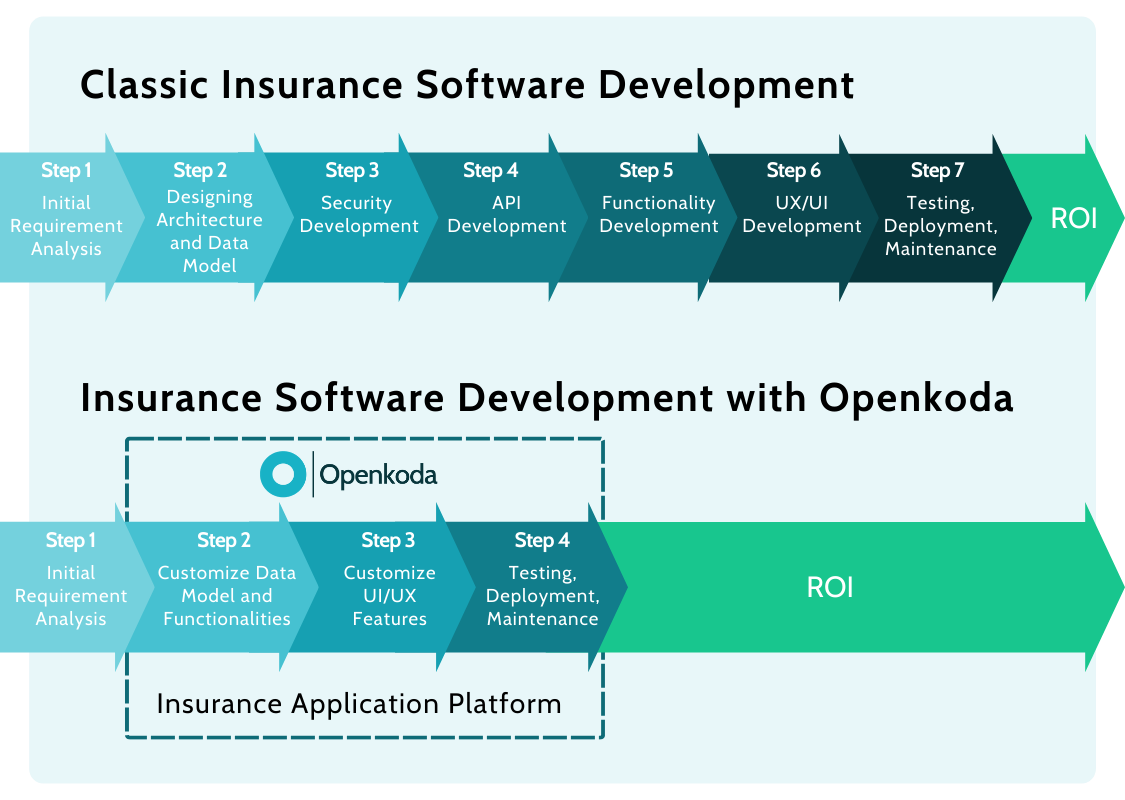
Teams can build internal tools, customer portals, dashboards, quote forms, and policy management systems using standard programming languages—without vendor lock-in.
The result is a highly customizable, scalable, and future-ready insurance system delivered in a fraction of the time required by traditional development methods.
So, how is this leap in speed and efficiency possible?
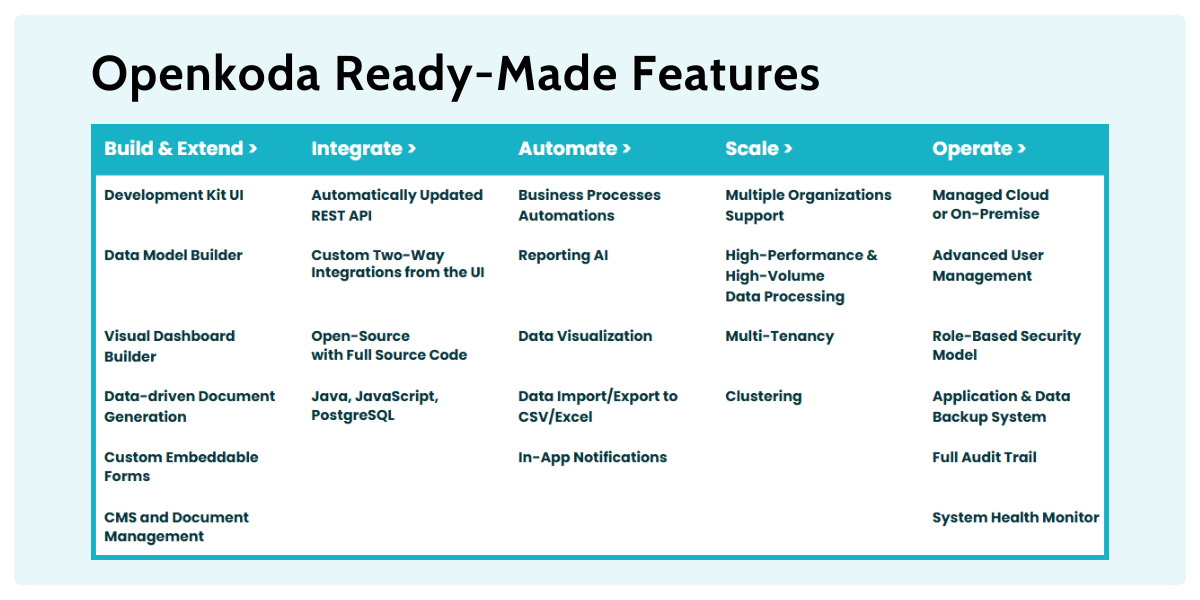
The key lies in a rich suite of ready-made functionalities—features that every enterprise insurance application needs to deliver from day one:
- Enterprise Application Foundation: ready-to-use building blocks like authentication, user management, multitenancy, and admin dashboard.
- Visual Data Model Builder: Modify and create data models using a visual UI with autocomplete, validation, and versioning.
- In-App Notifications: Notify specific users or entire organizations with custom messages via the platform.
- Claims Processing Template: Automate workflows, support AI-based decision-making, detect fraud, and speed up the end-to-end claims process.
- Policy Management Application Template: Manage policy lifecycles, automate renewals, handle templates, and ensure compliance with full customization options.
- Underwriting Dashboard
Visualize risk data, assess applications, and support underwriting decisions with real-time metrics and insights.
Trend #4: Self-Service for Policyholders
As digital-first expectations become the norm, policyholders increasingly prefer to manage their insurance needs independently—without phone calls, emails, or office visits.
By 2025, self-service capabilities are no longer a competitive advantage—they’re a baseline expectation. From policy updates to claims submissions, customers now demand seamless, anytime access across all devices.
Insurers that invest in strong self-service infrastructure can lower operational costs, enhancing customer satisfaction, and allowing agents to focus on higher-value interactions.
Essential Functionalities of Self-service Portals
An effective self-service portal must strike a balance between empowering users and maintaining simplicity. At its core, it should allow policyholders to manage the most common insurance tasks on their own, securely and efficiently.
Key features include:
- Policy management tools: Users should be able to view, download, and modify their active policies with ease.
- Claims processing: A step-by-step claims submission process with real-time status updates helps reduce support queries. It’s important as 78% of customers consider a smooth claims experience a key factor when choosing an insurer.
- Billing and payment access: Users should be able to view invoices, set up auto-pay, manage payment methods, and access billing history.
- Document repository: Centralized access to policy documents, coverage details, renewal notices, and communications.
- Live chat or chatbot assistance: Seamless access to help—whether via AI or human agents—for more complex queries.
- Secure login and identity verification: Ensuring data privacy through multi-factor authentication and secure session handling.
Designing a Frictionless User Experience: The Make-or-Break Factor
The success of any self-service platform hinges on its user experience (UX). Even the most feature-rich portal can fail if it’s slow, confusing, or unintuitive.
A well-designed UX allows policyholders to complete tasks effortlessly, boosting adoption and strengthening brand loyalty.
In a market where customer retention is closely tied to digital ease-of-use, insurers that prioritize UX in their self-service platforms will not only retain more customers but also stand out in an increasingly competitive landscape.
[Read also: Top 10 Insurance Software Development Companies in 2025]
Trend #5: Modernizing Legacy Insurance Systems
Many established insurers still rely on legacy insurance software systems built decades ago—never intended to meet today’s digital expectations.
The demand for seamless user experiences, faster product launches, and integration with modern insurtech ecosystems has highlighted the limitations of outdated infrastructure.
Insurers that delay insurance software modernization risk falling behind—both technologically and competitively.
Problems with Legacy Software in the Insurance Industry
Legacy systems may be the backbone of long-standing insurance operations, but they also represent major barriers to innovation and efficiency. Often built on outdated architectures and obsolete programming languages, these platforms create challenges across several critical areas:
- Slow product rollout: Launching or updating insurance products can take months, delaying time-to-market.
- Limited integration: Poor compatibility with modern APIs and digital platforms hinders scalability and partnerships.
- High maintenance costs: These systems require niche expertise and often lack vendor support, increasing operational expenses.
- Security risks: Older software is more vulnerable to cyber threats and often fails to meet current data protection standards.
- Outdated user experience: Both employees and customers face clunky interfaces and inefficient workflows, reducing satisfaction and productivity.
Ultimately, legacy software limits the insurer’s ability to compete in a fast-paced, customer-driven market. Without modernization, growth becomes reactive and constrained.
Modernizing Insurance Software Architecture
Modernizing core systems is no small task—it requires time, resources, and careful planning. But for insurers, it’s a strategic investment that delivers long-term gains in agility, customer satisfaction, and innovation capacity.
Forward-thinking insurers are now adopting modular, scalable platforms that support growth and change without major disruption—built on extendable, future-proof software foundations.
Platforms like Openkoda are playing a crucial role in this transformation.
As a high-performance, open-source application platform, Openkoda offers a robust foundation for modernizing enterprise-grade insurance systems. It enables insurers to:
- Rebuild legacy components incrementally using clean, maintainable code
- Leverage pre-built modules and workflows tailored to insurance use cases
- Maintain full architectural control and avoid vendor lock-in
- Accelerate development timelines and stay flexible for future updates

Trend #6: Usage-Based Insurance and Claims
Usage-based insurance (UBI) is one of the emerging technologies that is rapidly gaining traction across the insurance industry as customers increasingly seek more personalized—and above all—fairer pricing models.
How does it work?
Rather than relying solely on generalized risk profiles and static premiums, UBI uses real-time or near-real-time data—often gathered via telematics, mobile apps, or IoT devices—to adjust coverage and pricing based on actual behavior and usage patterns.
UBI is especially popular in car insurance, where factors like speed, distance, and braking habits are tracked to reward safe driving with lower premiums. For instance, a customer who drives infrequently and avoids high-risk areas during peak hours may pay significantly less than someone with riskier driving habits.
But UBI is also expanding into health, property, and travel insurance.
Fitness trackers, smart home sensors, and travel data are increasingly being used to tailor policies, pricing, and insurance claims processes.
Naturally, this model raises questions about data privacy and security—an area that insurers must address transparently to build and maintain customer trust.
Enabling Real-Time Claims and Risk Evaluation
One of the key advantages of usage-based insurance is its ability to streamline claims management through real-time data capture. Using sensors, mobile apps, or connected devices, insurers can often detect incidents—such as car accidents or home flooding—and automatically initiate the claims process.
This proactive approach enhances speed, accuracy, and transparency, helping reduce fraud and strengthen customer trust.
Building Flexible, Data-Driven Insurance Products
Usage-based models require insurers to rethink how they design and deliver products.
Rather than offering one-size-fits-all policies, insurers must develop flexible product structures that can dynamically adapt to individual behavior and real-time context.
This demands flexible core platforms that support customizable business rules and workflows—enabling insurers to adjust coverage logic based on real-time events without compromising performance, scalability, or security.
Trend #7: Emerging Risks
As the world becomes more interconnected and unpredictable, insurers are facing a wave of new and rapidly evolving risks that were not on the radar a decade ago.
In 2025, two categories in particular—climate-related risks and cyberthreats—are at the forefront of reshaping how insurers assess exposure, design coverage, and respond to claims.
The average number of severe natural disasters in the US rose from five (1980-2010) to 28 (2024). Last year, losses from natural disasters reached a staggering $80 billion, driving up premiums across the country and prompting some carriers to stop offering coverage.
Cybercrime is also on the rise.
In the United States, IC3 complaints almost doubled, and losses nearly quadrupled between 2019 and 2023.
Challenges and Opportunities
The rise of emerging risks presents insurers with a dual-edged reality—significant challenges, but also unprecedented opportunities for innovation and growth.
Key challenges include:
- Data limitations and unpredictability: Emerging risks like cyberattacks and climate events don’t follow predictable patterns, making it difficult to model them using traditional actuarial methods.
- Coverage gaps and exclusions: Many existing insurance policies were not designed with today’s risks in mind, leading to disputes, denied claims, or underinsurance.
- Regulatory complexity: Governments and regulators are beginning to mandate disclosures and controls related to climate risk and cybersecurity, requiring insurers to stay ahead of evolving compliance standards.
- Operational readiness: Responding to high-frequency events (like repeated cyber breaches) requires new infrastructure and claims-handling capabilities that legacy systems may not support.
Opportunities, however, are equally compelling:
- Product innovation: There is strong market demand for new insurance offerings, from parametric climate coverage to cyber insurance for SMEs and gig workers.
- Value-added services: Insurers can move beyond indemnification by offering prevention, monitoring, and risk mitigation services—enhancing customer loyalty and creating new revenue streams.
- Data-driven differentiation: By leveraging external data, machine learning, and insurtech platforms, insurers can offer more personalized, accurate, and responsive products than ever before.
- Market expansion: Businesses and individuals previously not covered for certain risks are now actively seeking protection—unlocking new customer segments and distribution opportunities.
Successfully navigating these emerging risks requires a mindset shift—from risk avoidance to risk management and innovation. Insurers that embrace this shift will lead the next era of industry transformation.
How Insurers Should Adapt to Emerging Risks
To remain relevant and resilient in this changing landscape, insurers must:
- Develop agile product frameworks that can quickly adapt to new risk categories or regulatory requirements.
- Leverage external data sources (e.g., weather intelligence, cybersecurity threat databases) to improve risk assessment and pricing models.
- Invest in predictive analytics and AI to spot emerging trends and respond proactively.
- Partner with industry experts and insurtech platforms to co-create niche or parametric insurance offerings tailored to specific risk events (e.g., insuring against a predefined level of rainfall or a cyber breach severity score).
Conclusion: Future-Ready Insurers Will Be Tech-Driven, Agile, and Customer-Centric
From embedded insurance to AI automation and usage-based models, insurers are reimagining how they operate and deliver value.
One thing is clear: digital innovation is no longer optional—it’s essential for staying competitive.
But with innovation comes complexity. Balancing personalization, privacy, speed, and the human touch requires smart strategy and strong tech partners.
Those who move fast, adapt often, and build with the customer in mind will lead the future of insurance.