
Embedded Insurance: Key Statistics, Trends and Forecasts
Embedded insurance is rapidly transforming how consumers interact with insurance products, adding coverage options directly into the purchase of goods and services.
Let’s explore the key statistics, trends, and forecasts shaping this rapidly growing sector.
Rise of Embedded Insurance: Game Changer for The Insurance Industry
Embedded insurance refers to the seamless integration of insurance products directly into the purchase journey of other goods or services.
Instead of buying insurance separately, companies offer customers coverage at the point of sale – whether they are booking a flight, renting a car or buying electronics.
In 2024, it will be one of the hottest trends transforming the insurance industry.
For insurers, it opens up new distribution channels, giving them access to customers they might not otherwise have reached.
For consumers, it simplifies the decision-making process and offers convenience by eliminating extra steps.
By embedding insurance into everyday transactions, companies are redefining how insurance is thought about and sold, making it more accessible and personalized than ever.
State of Embedded Insurance Market: Statistics and Insights
There are many optimistic predictions about the growth potential of embedded insurance.
The rapid growth of embedded insurance is fueled primarily by changing consumer behavior and the digitization of industries, but also by insurers’ never-ending race to close the global protection gap.
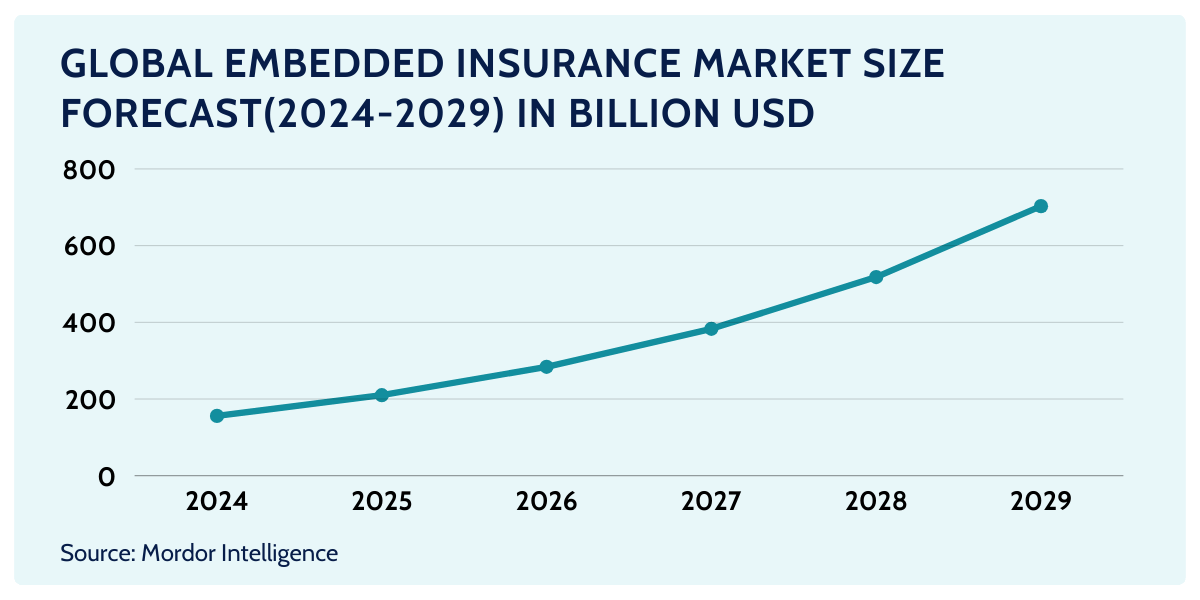
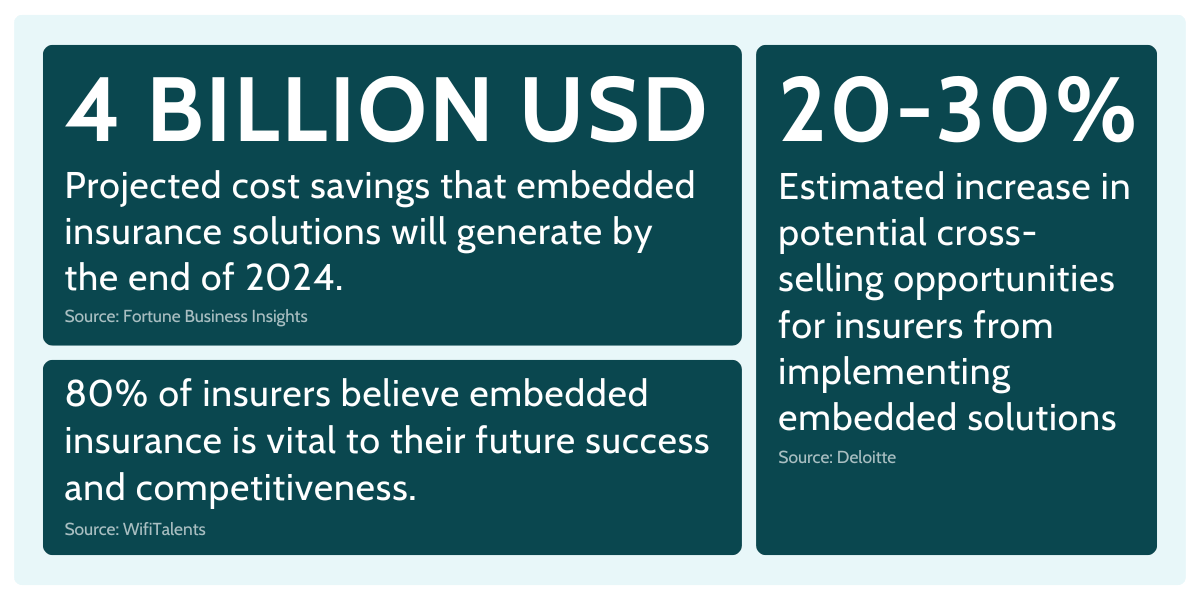
The global embedded insurance market is projected to reach approximately $700 billion in gross written premiums (GWP) by 2030, more than six times its current size. By 2033, it is projected to account for 15% of global GWP, reaching approximately $1.1 trillion, up from its current 3-5%.
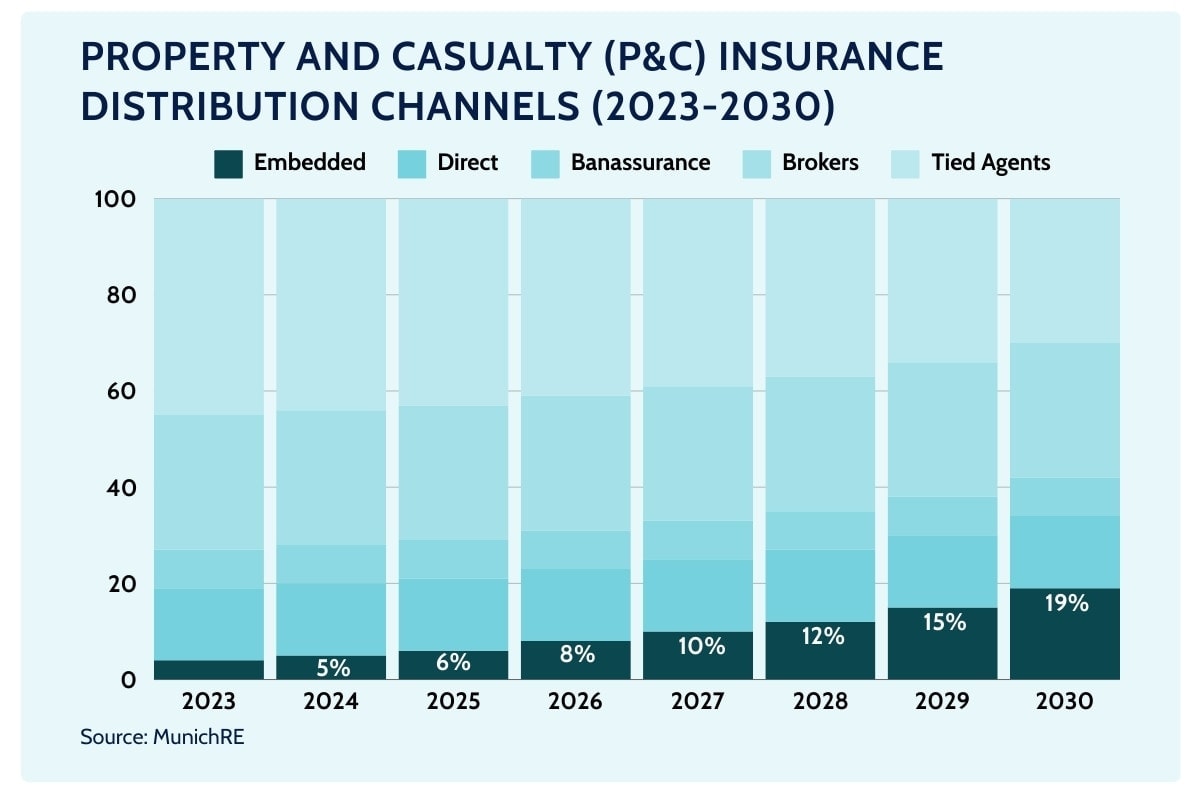
According to Swiss Re, in certain P&C markets this would likely be nearer 30% of the total, taking share in particular from tied insurance agents and branch channels.
This shift is also creating new distribution channels for insurers, with non-insurance brands potentially selling up to $5 trillion in insurance by 2032.
This opens up huge opportunities for companies, as embedded insurance not only enhances the customer experience, but also allows insurers to access a wider market through digital platforms.
With 94% of insurance executives viewing embedded insurance as critical to future strategies, the industry is clearly betting on this model to redefine how insurance is bought and sold, moving away from traditional distribution methods and aligning with modern consumer expectations.
The growth of embedded insurance is particularly strong in regions such as Asia, where high smartphone penetration rates and a significant underinsured population present huge opportunities for digital insurance solutions.
Here, platforms such as ecommerce and ride-hailing apps are integrating insurance offerings, making them more accessible and affordable for users.
Technological innovations, such as AI and data-driven insurance underwriting, are further improving the scalability and customization of these embedded insurance products.
What’s next? Future Embedded Insurance Trends
The future of embedded insurance is poised for continued innovation and expansion, driven by significant investments and technological advancements.
In the first three quarters of 2023 alone, insurtech investments reached an all-time high of $8.1 billion, compared to just $140 million a decade earlier. This influx of capital has fueled innovations in areas like cloud computing, AI-powered solutions, and most notably, embedded insurance.
Artificial Intelligence and Hyper-personalization
Looking ahead, hyper-personalization will be a key trend, with insurers using AI and big data to offer tailored solutions and enhance customer experiences.
At the same time, AI’s operationalization in claims processing, risk assessment, and customer engagement will further differentiate forward-thinking insurers.
Platforms like Openkoda provides features such as Reporting AI, allowing businesses to generate complex SQL queries and analyze data using natural language, making it easier to create tailored solutions without needing extensive technical knowledge.
By 2025, these AI technologies are expected to redefine how insurers interact with customers, making processes faster, more accurate, and customer-friendly.
With such rapid advancements, embedded insurance will continue to play a pivotal role across sectors like automotive, healthcare, and e-commerce.
Embedded 3.0
Another emerging trend in the insurance industry is Embedded Insurance 3.0, a significant leap from its earlier generations.
This phase focuses on hyper-personalization and real-time data integration, allowing insurers to offer highly tailored, on-demand insurance solutions.
Unlike Embedded Insurance 1.0, which involved simply bundling insurance with other products, and Embedded Insurance 2.0, which scaled this integration across various platforms, Embedded Insurance 3.0 integrates coverage into the background of a service or product with little to no input from the consumer.
This shift offers hyper-personalization and real-time integration using technologies like AI, IoT, and big data.
Embedded Insurance: a Win-win Solution for Everyone
What’s special about embedded insurance is that it creates value for clients, companies, and insurance industry as a whole. Let’s take a closer look at some examples:
Benefits for Insurers and Retailers
For insurers, embedded insurance provides a valuable new distribution channel that extends customer reach and drives higher conversion rates.
By partnering with non-insurance companies, insurers can reach new customer bases through channels such as e-commerce, travel and automotive, increasing their visibility and sales.
One of the most significant benefits is the reduction of customer acquisition costs.
In the UK, for example, partnerships through embedded insurance models can reduce these costs by 75%, from £200 to £50 per customer. This is a game changer for insurers looking to scale efficiently, as traditional marketing and outreach can be both time consuming and expensive.
Embedded insurance also increases customer engagement and conversion rates.
Offering insurance at the point of sale can increase purchase intent by as much as 25%, reflecting the convenience and relevance of seamlessly integrating coverage into the buying process.
In addition, many insurers are already recognizing the value of partnerships in this space, with approximately 63% of insurers now partnering with industries such as e-commerce, automotive, and healthcare to leverage their platforms to reach broader customer bases.
These partnerships enable insurers to offer tailored products at the right time, improving the customer experience and maximizing market penetration.
[Read also: Digital Transformation in Insurance Industry: Key Strategies & Trends]
Benefits for Customers
The basic idea behind embedded insurance solutions is to offer convenience and simplicity by integrating insurance directly into the purchase of everyday products and services, such as cars, electronics or travel bookings.
As the world becomes increasingly digital, the options available to customers are rapidly expanding to keep pace with their growing expectations.
Younger, digitally native generations such as Millennials and Gen Z will soon make up a significant portion of the workforce, and they have little patience for outdated, paper-based processes.
This is why embedded insurance policies are so promising for the future — they offer seamless, integrated solutions that meet the demand for convenience and simplicity in a digital-first world.
As a result, businesses that integrate insurance seamlessly into their digital offerings stand to benefit from increased customer satisfaction and higher conversion rates.
According to Sapiens Observatory, over 60% of customers would purchase insurance from an online retailer if it were offered at checkout, and 78% would be more inclined to spend more if extended warranties were available at the same point of sale.

How Different Industries Leverage Embedded Insurance
Automotive: a Segment in Revolution
The automotive sector is a place where embedded insurance solutions are already quite mature, with many manufacturers offering extended warranties and customized coverage when ordering a vehicle.
But innovation doesn’t stop there, as a smart pay-as-you-drive (PAYD) car insurance coverage model has emerged as an innovative and promising insurance solution.
How does it work?
This insurance model relies on telematics devices installed in vehicles that monitor driving behavior, such as speed, braking and acceleration, to more accurately assess risk.
Tesla is considered a pioneer in this approach, as its embedded insurance system integrates directly with its vehicles’ built-in telematics.

Tesla’s real-time insurance calculates premiums based on individual driving metrics, including factors such as harsh braking, aggressive turning, and unsafe following distances. Unlike traditional insurance, Tesla’s system focuses on driving behavior, offering potential savings of 20-60% for safer drivers.
The company reports that drivers using Tesla’s Safety Score system are 30% less likely to be involved in a collision, underscoring its effectiveness in promoting safer driving.
According to a Statista report, the PAYD insurance market is expected to grow globally to $15.6 million by 2028. According to a Deloitte report, PAYD embedded insurance model can lead to a 20-30% reduction in road accidents and a 10-30% decrease in miles driven.
Deloitte predicts that if as much as 20% of the US personal auto market goes the embedded route by 2030, at least US$50 billion in premiums could be diverted away from the industry’s traditional distribution channels.
To see how your company can quickly set up and deploy embeddable insurance forms for car insurance just like Tesla, Stellantis or Rivian, check out this quick demo:
Ecommerce: Improving Profit Margins With Embedded Insurance
As online retailers with increasingly narrow profit margins strive to stay competitive in the ecommerce market, many are turning to add-on services like theft and damage protection at the point of sale to boost their offerings.
Embedded insurance adds significant value to the ecommerce sector by providing retailers with new revenue streams while enhancing the customer experience.
By offering protection plans as part of the checkout process, product or service provider can not only increase customer satisfaction but also drive additional sales.
According to 2022 research from one of America’s top 15 retailers, sales of protection plans accounted for 1.4% of the company’s total revenue—amounting to all thanks to offering embedded insurance at checkout. $725 million
This demonstrates how embedded insurance can be a powerful tool for ecommerce platforms to diversify income and improve profitability without disrupting the purchasing journey.
Travel: Its All About Ensuring Smooth Journey
The COVID-19 pandemic of 2020 drastically changed the face of travel, putting protection at the forefront of every traveler’s concerns—not only for health-related risks but also for cancellations and unexpected changes.
Travel insurance has evolved from an optional add-on to an essential component of travel planning. Today, it must be comprehensive, covering all types of uncertainties and potential disruptions.
Embedded insurance plays a critical role in meeting these needs seamlessly.
By integrating protection directly into the booking process, whether it’s for flights, hotels, or other travel services, customers gain peace of mind without having to search for third-party providers.
[Read also: AI-Driven Insurance Analytics: Faster, Better, Smarter]
How Can Your Business Introduce Embedded Insurance?
To introduce embedded insurance into your business, leveraging platforms like Openkoda can significantly accelerate the development process.
Openkoda provides a flexible, open-source solution using which you can build your own, customizable embedded insurance solution that can easily integrate with any platform.
Thanks to its open-source core it eliminates popular issues like vendor lock-in and user based pricing.
With Openkoda you can streamline the development of custom insurance software, especially embedded systems, while reducing time-to-market and development costs, making it easier to meet evolving customer demands for convenience and personalization.
